「CF486D」Valid Sets
As you know, an undirected connected graph with n nodes and n - 1 edges is called a tree. You are given an integer d and a tree consisting of n nodes. Each node i has a value ai associated with it.
We call a set S of tree nodes valid if following conditions are satisfied:
- S is non-empty.
- S is connected. In other words, if nodes u and v are in S, then all nodes lying on the simple path between u and v should also be presented in S.
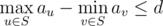 .
.
Your task is to count the number of valid sets. Since the result can be very large, you must print its remainder modulo1000000007 (109 + 7).
The first line contains two space-separated integers d (0 ≤ d ≤ 2000) and n (1 ≤ n ≤ 2000).
The second line contains n space-separated positive integers a1, a2, …, an(1 ≤ ai ≤ 2000).
Then the next n - 1 line each contain pair of integers u and v (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n) denoting that there is an edge between u and v. It is guaranteed that these edges form a tree.
Print the number of valid sets modulo 1000000007.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
1 4 2 1 3 2 1 2 1 3 3 4 |
|
1 |
8 |
|
1 2 3 4 |
0 3 1 2 3 1 2 2 3 |
|
1 |
3 |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
4 8 7 8 7 5 4 6 4 10 1 6 1 2 5 8 1 3 3 5 6 7 3 4 |
|
1 |
41 |
In the first sample, there are exactly 8 valid sets: {1}, {2}, {3}, {4}, {1, 2}, {1, 3}, {3, 4} and {1, 3, 4}. Set {1, 2, 3, 4}is not valid, because the third condition isn’t satisfied. Set {1, 4} satisfies the third condition, but conflicts with the second condition.
枚举点权的下界,然后直接树形dp
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 |
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<algorithm> #include<queue> #include<cmath> #include<map> #include<queue> #define mod 1000000007 #define inf 2000000000 #define ll long long using namespace std; inline ll read() { ll x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} return x*f; } int d,n,cnt; int last[2005],a[2005]; ll f[2005],ans; bool vis[2005]; struct data{int to,next;}e[4005]; void insert(int u,int v) { e[++cnt].to=v;e[cnt].next=last[u];last[u]=cnt; e[++cnt].to=u;e[cnt].next=last[v];last[v]=cnt; } void dfs(int x,int l,int r,int fa) { f[x]=1; for(int i=last[x];i;i=e[i].next) if(!vis[e[i].to]&&a[e[i].to]>=l&&a[e[i].to]<=r&&e[i].to!=fa) { dfs(e[i].to,l,r,x); f[x]*=f[e[i].to]+1; f[x]%=mod; } } void cal(int x) { memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) if(a[i]==x) { vis[i]=1; dfs(i,x,x+d,0); ans=(ans+f[i])%mod; } } int main() { d=read();n=read(); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)a[i]=read(); for(int i=1;i<n;i++) { int u=read(),v=read(); insert(u,v); } for(int i=0;i<=2000;i++) cal(i); printf("%lld",ans); return 0; } |
