「CF433C」Ryouko’s Memory Note
Ryouko is an extremely forgetful girl, she could even forget something that has just happened. So in order to remember, she takes a notebook with her, called Ryouko’s Memory Note. She writes what she sees and what she hears on the notebook, and the notebook became her memory.
Though Ryouko is forgetful, she is also born with superb analyzing abilities. However, analyzing depends greatly on gathered information, in other words, memory. So she has to shuffle through her notebook whenever she needs to analyze, which is tough work.
Ryouko’s notebook consists of n pages, numbered from 1 to n. To make life (and this problem) easier, we consider that to turn from page x to page y, |x - y| pages should be turned. During analyzing, Ryouko needs m pieces of information, the i-th piece of information is on page ai. Information must be read from the notebook in order, so the total number of pages that Ryouko needs to turn is 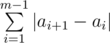 .
.
Ryouko wants to decrease the number of pages that need to be turned. In order to achieve this, she can merge two pages of her notebook. If Ryouko merges page x to page y, she would copy all the information on page x to y (1 ≤ x, y ≤ n), and consequently, all elements in sequence a that was x would become y. Note that x can be equal to y, in which case no changes take place.
Please tell Ryouko the minimum number of pages that she needs to turn. Note she can apply the described operation at most once before the reading. Note that the answer can exceed 32-bit integers.
The first line of input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105).
The next line contains m integers separated by spaces: a1, a2, …, am (1 ≤ ai ≤ n).
Print a single integer — the minimum number of pages Ryouko needs to turn.
|
1 2 |
4 6 1 2 3 4 3 2 |
|
1 |
3 |
|
1 2 |
10 5 9 4 3 8 8 |
|
1 |
6 |
In the first sample, the optimal solution is to merge page 4 to 3, after merging sequence a becomes {1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 2}, so the number of pages Ryouko needs to turn is |1 - 2| + |2 - 3| + |3 - 3| + |3 - 3| + |3 - 2| = 3.
In the second sample, optimal solution is achieved by merging page 9 to 4.
题解
将数列中的某一些相同的数全替换成一个数
使得数列俩俩差值和最小
一开始看成替换一个数了
真是坑爹
好像就是把相同的数用链表挂起来
然后枚举替换某一个数x
将x链表中的所有x相邻的且不等于x的放进数组
取一个数使得其到这些数的距离和最小
即排序后取中位数y,也就是x要替换成的数
扫一遍得出将x替换成y所能减少的ans
取一个能减少最多的x
就这样
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 |
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<ctime> #define inf 0x7fffffff #define linf 9223372036854775807LL #define ll long long using namespace std; inline int read() { int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} return x*f; } int n,m,cnt; ll ans,mx,sum,tmp; int a[100005],head[100005],next[100005]; int b[100005]; ll max(ll a,ll b){return a>b?a:b;} int main() { n=read(),m=read(); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) { a[i]=read(); next[i]=head[a[i]];head[a[i]]=i; if(i!=1)ans+=abs(a[i]-a[i-1]); } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { sum=tmp=0; int x=0; for(int j=head[i];j;j=next[j]) { if(j>1&&a[j-1]!=i)b[++x]=a[j-1],sum+=abs(b[x]-i); if(j<m&&a[j+1]!=i)b[++x]=a[j+1],sum+=abs(b[x]-i); } sort(b+1,b+x+1); int t=b[x/2+1]; for(int k=1;k<=x;k++) tmp+=abs(b[k]-t); mx=max(mx,sum-tmp); } printf("%I64d",ans-mx); return 0; } |
